|
Stress means:additional internal forces that per unit area bears.The formular is: |
|
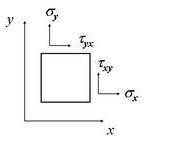
Normal stress and sheat stress When the material under the external force can not occur displacement, its geometric shape and size will change, this deformation is called strain.The internal occur the same size and opposite reaction against external forces when the deformtion appears. The distribution of internal forces at a point known as the set degree of stress.the product of stress and the micro-area is Micro internal force.Or because of external factors (stress, humidity, etc.) that objects appear deformation and among various parts of the objects produce internal forces, to resist this external effect, and endeavor to make the object from the position after deformation returned to pre- position. In the study of a point on the internal force per unit area in cross-sectional is called stress. In accordance with the direction of stress and strain relations, stress can be divided into the direct stress σ and shear stress τ, the direction of direct stress is parallel to strain directions, and the direction of shear stress and strain is vertical.In according to the different form of load, the stress can be divided into tensile compressive stress,bending stress and torsion stress. Stress classification Normal stress and sheat stress Direct stress and shear stress Some materials in the work, the external force have no change over time, then the size of its internal stress have no changes, known as the static stress; there are some other materials, external forces suffered periodic change with time, then internal stress also changes periodically with time, known as the alternating stress.Materials under alternating stress as fatigue damage. Usually the alternating stress is much smaller than its ultimate strength under static load, the damage may occur. In addition, the material will enlarge internal due to the section size change. This phenomenon called stress concentration. For the uniform and brittle materials, the stress concentration will greatly reduce the intensity of component,which should pay special attention to the component. When the objects be forced will occur deformation, the inner deformation of each point generally not the same. To describe the point on the degree of deformation of the mechanical quantity is the point of strain.Therefore, we can compare the size and shape with before. Linear strain When taking the cell cube as regular hexahedr in the rectangular coordinates, the ratio of the changes and the original length of the length of three mutually perpendicular edges,defined as the linear strain,with ε. .A point in x、y、z direction of the line of strain were εx、εy、εz.The linear strain response to elongation is positive,rduce is the negative.Shear strain Units of two mutually perpendicular edge, right-angle change value after deformation, defined as the angle strain or shear strain, with γ said.The shear strain of a point in the x-y direction,y-z direction and z-x direction.respectively γxy、γyz、γzx. To reduce the shear angle is positive, otherwise negative. Point of the strain state When known the point of the strain component εx, εy, εz, γxy, γyz, γzx, the point in any direction in the linear strain, and any two line segments through the point of change in volume between the right angle, can according to the coordinate transformation formula of the strain components obtained. The strain state of this points is fixed. Measuring Tools Strain gauge is an instrument to measure transparent objects that due to internal stress bring the birefringence phenomenon.The source of the birefringence is due to the uniform cooling or external mechanical effects. |
| Previous (The impact to the organization and property of the heat treatment of D2 steel’s quenching and backdraft) |