|
The impact to the organization and property of the heat treatment of D2 steel's quenching and backdraft preface |
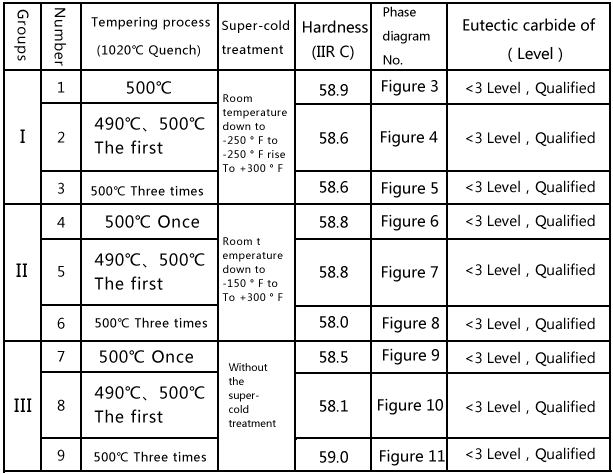 |
| 3.Result analysis 1. The unevenness of eutectic carbide of steel meet the technical standards 2. From the sheet1,the hardness of 3 categery and 9 samples are 58.5+-0.5HRC ,the hardness does't increase after ultra-cold treatment.,why? We have mentioned in the basic theory:Ultra-cold treatment is to make the low hardness of residual austenite to turn into the higher hardness of martensite after quenching and backfire.Obviously,the premise is how many residual austenite before ultra-cold treatment? The amount of retained austenite related to quenching temperature and tempering temperature (and frequency) .There is two element to influence the volume of austenite: I.Adoptint the low quenching temperature (1020.c),that is the austenite alloying is low,the volume of austenite is less (about 12~13% ) 2.Processing the backfire (500.C),most of the austenite had turned into martensite (500.C,one time backfire,the residual austenite is about 3% after ultra-cold treatment,tempering after 2 to 3 times,the amount of residual austenite become less than before),Therefore, even if the residual austenite about 3% all turn into quenching martensite after ultra-cold treatment, there is minimal impact to hardness If use 1050 .c for quenching.the amount of retained austenite up to 23%, and the tempered by the lower temperature (eg 400 .c or less) ,the amount of residual austenite is large, the hardness of mould is not high (about 57 ~ 58HRC),then if process the ultra-cold treatment ,more residual austenite will turn into martensite,and the hardness will increase. 4ЎўAbout deformation Mechanical parts, molds and other frequently during the placement and use of difference sizes, deformation or even cracking, which relate to the stable organization, backfire not enough or the stree does't eliminate after heat treatment.For example,unstable residual austenite will turn into quenching marstesite in a certain external conditions (temperature,stress),due to additional stress in tissue volumn,and the quenching marstesite is an unstable organization,withour the appropriate temper,the brittleness is high,and also have damaging. So on the precision parts,mold deformation,overproof,more retained austenite after heat treatment,one of the reasons is the unstable organization.After ultra-cold treatment,the residual austenite will turn into quenching martensite as far as possible,and it is an effective method of stabilizing the organization after quenching martenisite and tempering again.of course,precision mold and parts duing the placement and using will appear overproof,deformation, and one of the element that make the tissue unstable is over amount of residual austenite.The metallurgical quality of steel,for example,the homogeneity of high-chromium will influence the distribution of residual austenite after heat treatment and ultra-cold treatment,also is another element influencing the deformation degreen. Conclusion: The submit for censorship of the steel was not found the phenomenon that the hardness improve after ultra-cold treatment,it is because of the original lower quenching temperature, a relatively small amount of residual austenite after quenching ,in addition,it had backfired before ultra-cold treatment,small amount of residual austenite,so the cold treatment is also a small amount into martenisite,the hardness is minimal. The premise that make the hardness increase after ultra-cold treatment is:there is large amount of residual austenite before handling ultra-cold treatment,while the amount of residual austenite is relate to the heat treatment and backfire. The residual austenite is an unstable organization,its existence will influence the stability of the organization,during the process that turn into martensite ,this phenomenon will occur,due to the changes in specific volume.We should minimize the volume of austenite to the precision parts which have size requirements. Mechanical Engineering Department Of South China University of Technology |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Next note(Definition of Stress) |

